Vue组件中实现LLM流式输出的打字效果
前言
在构建AI聊天应用时,实现一个流畅的打字效果对提升用户体验至关重要。本文将详细拆解一个Vue组件中实现大语言模型(LLM)流式输出打字效果的核心原理和实现方法。
核心思想
实现打字效果的核心思想是将收到的流式内容转换为字符级队列,然后通过控制队列的处理速度来模拟打字效果。整个流程可以分为以下几个关键步骤:
- 接收流式内容
- 将内容转换为字符级队列
- 控制队列处理速度实现打字效果
- 处理特殊内容(代码块、HTML标签等)
- 与Markdown渲染器结合
数据结构设计
首先,我们需要设计几个关键的数据结构:
// 打字内容队列
const typingQueue = ref([]);
// 是否正在执行打字效果
const isTyping = ref(false);
// 打字速度
const typingSpeed = ref(25);
// 用于保存当前已显示的内容
const currentContentBuffer = ref("");
// 最终显示的内容
const displayContent = ref("");
这些响应式数据共同构成了打字效果系统的状态管理核心。
流式内容处理
当接收到流式内容时,我们需要判断这是初始内容还是增量更新:
const processStreamContent = (newContent) => {
// 如果内容没有变化,直接返回
if (newContent === currentContentBuffer.value) {
return;
}
// 首次内容处理
if (currentContentBuffer.value === "") {
// 创建完整字符队列
createCharacterQueue(newContent);
} else {
// 增量更新处理
const prevLength = currentContentBuffer.value.length;
if (newContent.length > prevLength) {
// 只处理新增的部分
const newPart = newContent.substring(prevLength);
createCharacterQueue(newPart, true);
} else if (newContent.length < prevLength) {
// 内容变短,可能是因为修正了之前的内容,重新设置
displayContent.value = newContent;
currentContentBuffer.value = newContent;
typingQueue.value = [];
} else {
// 内容长度相同但不同,直接更新
if (newContent !== currentContentBuffer.value) {
displayContent.value = newContent;
currentContentBuffer.value = newContent;
}
}
}
};
这个函数处理三种情况:
- 首次接收内容
- 增量更新(新内容添加)
- 内容修正(内容变短或完全替换)
字符级队列创建
为了实现平滑的打字效果,我们需要将内容转换为字符级队列:
const createCharacterQueue = (content, isIncremental = false) => {
if (!content) return;
// 避免重复内容处理
if (isIncremental && typingQueue.value.length > 0) {
if (typingQueue.value.some((item) => item === currentContentBuffer.value)) {
typingQueue.value = [];
}
}
let buffer = isIncremental ? currentContentBuffer.value : "";
// 检查是否包含特殊内容
const hasCodeBlock = content.includes("```") || content.includes("<pre>");
const hasHtmlTags = /<[^>]*>/.test(content);
// 动态调整块大小
let chunkSize = 1; // 默认1个字符一组
if (content.length > 1000) {
chunkSize = hasCodeBlock || hasHtmlTags ? 2 : 3;
} else if (content.length > 500) {
chunkSize = hasCodeBlock || hasHtmlTags ? 1 : 2;
}
if (hasCodeBlock || hasHtmlTags) {
// 特殊内容处理(保持标签完整性)
const specialChunks = splitContentWithSpecialTags(content);
let currentBuffer = buffer;
for (const chunk of specialChunks) {
currentBuffer += chunk;
typingQueue.value.push(currentBuffer);
}
} else {
// 普通文本按字符切分
for (let i = 0; i < content.length; i += chunkSize) {
const chunk = content.substring(
i,
Math.min(i + chunkSize, content.length)
);
const newText = buffer + chunk;
buffer = newText;
typingQueue.value.push(newText);
}
}
// 确保队列中没有重复项
typingQueue.value = [...new Set(typingQueue.value)];
// 启动打字效果处理
if (!isTyping.value) {
isTyping.value = true;
processTypingQueue();
}
};
这个函数的关键点是:
- 根据内容长度和类型动态调整块大小
- 对代码块和HTML标签等特殊内容进行特殊处理
- 避免队列中的重复内容
特殊内容处理
对于代码块和HTML标签,我们需要特殊处理以保持它们的完整性:
const splitContentWithSpecialTags = (content) => {
// 匹配HTML标签、代码块和普通文本
const tagRegex = /(<[^>]*>|```[^`]*```|`[^`]*`)/g;
const chunks = [];
let lastIndex = 0;
let match;
// 查找所有特殊标记
while ((match = tagRegex.exec(content)) !== null) {
// 添加标记前的普通文本(按字符分割)
const textBefore = content.substring(lastIndex, match.index);
if (textBefore) {
// 普通文本按字符添加
for (let i = 0; i < textBefore.length; i += 2) {
chunks.push(
textBefore.substring(i, Math.min(i + 2, textBefore.length))
);
}
}
// 添加特殊标记(保持完整)
chunks.push(match[0]);
lastIndex = match.index + match[0].length;
}
// 添加最后一部分文本
const remainingText = content.substring(lastIndex);
if (remainingText) {
for (let i = 0; i < remainingText.length; i += 2) {
chunks.push(
remainingText.substring(i, Math.min(i + 2, remainingText.length))
);
}
}
return chunks;
};
这个函数确保HTML标签和代码块等特殊内容作为完整的单元被处理,避免标签被拆分导致的渲染问题。
队列处理与打字效果实现
处理队列是实现打字效果的核心:
const processTypingQueue = () => {
// 队列为空,停止打字效果
if (typingQueue.value.length === 0) {
isTyping.value = false;
return;
}
// 处理队列中的下一个内容
isTyping.value = true;
const contentChunk = typingQueue.value.shift();
// 跳过重复内容
if (contentChunk === currentContentBuffer.value) {
window.requestAnimationFrame(processTypingQueue);
return;
}
// 使用 requestAnimationFrame 减少重绘
window.requestAnimationFrame(() => {
// 更新显示内容
currentContentBuffer.value = contentChunk;
displayContent.value = contentChunk;
// 动态调整速度:队列越多,速度越快
const totalLength = typingQueue.value.length;
let dynamicDelay = 15; // 默认值
if (totalLength > 500) {
dynamicDelay = 5; // 很多内容时非常快
} else if (totalLength > 200) {
dynamicDelay = 8; // 较多内容时较快
} else if (totalLength > 50) {
dynamicDelay = 12; // 中等内容时中速
} else if (totalLength > 10) {
dynamicDelay = 16; // 少量内容时略慢
}
// 计算下一次处理的延迟
setTimeout(() => {
requestAnimationFrame(processTypingQueue);
}, dynamicDelay);
});
};
这个函数的亮点是:
- 使用
requestAnimationFrame优化性能 - 根据队列长度动态调整打字速度
- 跳过重复内容处理
内容监听与更新
我们需要监听内容变化,以便在收到新内容时触发处理:
watch(
() => props.content,
(newContent, oldContent) => {
// 内容未变化,不需要处理
if (newContent === oldContent) {
return;
}
// 处理空消息
if (!newContent) {
if (markdownRenderer && typeof markdownRenderer.clear === "function")
markdownRenderer.clear();
clearTypingContent();
return;
}
// 用户消息或错误消息仍然使用原有方式
if (props.type !== "assistant" || props.error) {
clearTypingContent();
displayContent.value = newContent;
currentContentBuffer.value = newContent;
return;
}
// 如果不是流式输出
if (!props.streaming) {
// 如果内容未变化或者已经处理过,无需再次处理
if (newContent === currentContentBuffer.value) {
return;
}
clearTypingContent();
displayContent.value = newContent;
currentContentBuffer.value = newContent;
// 如果渲染器存在,也更新渲染内容
if (markdownRenderer && typeof markdownRenderer.render === "function") {
try {
if (typeof markdownRenderer.clear === "function")
markdownRenderer.clear();
markdownRenderer.render(newContent);
} catch (error) {
console.error("渲染内容出错:", error);
}
}
return;
}
// 以下处理流式输出
const isInitialContent = !oldContent || oldContent.trim() === "";
if (isInitialContent) {
// 只有初次接收内容时才清空之前的状态
clearTypingContent();
}
// 打字效果处理
try {
processStreamContent(newContent);
} catch (error) {
console.error("处理流式内容时出错:", error);
// 降级处理:直接设置内容
displayContent.value = newContent;
currentContentBuffer.value = newContent;
}
// 渲染器增量更新
if (markdownRenderer && typeof markdownRenderer.render === "function") {
try {
// 计算新增的内容
const prevLength = oldContent ? oldContent.length : 0;
if (newContent.length > prevLength) {
const increment = newContent.substring(prevLength);
// 避免重复处理
if (increment.trim()) {
// 使用渲染器处理
markdownRenderer.render(increment);
}
} else if (
newContent.length < prevLength ||
newContent !== oldContent
) {
// 内容变短或完全不同,全量渲染
if (typeof markdownRenderer.clear === "function")
markdownRenderer.clear();
markdownRenderer.render(newContent);
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("使用渲染器处理内容时出错:", error);
// 渲染器失败,回退到基本处理
displayContent.value = newContent;
currentContentBuffer.value = newContent;
markdownRenderer = null;
}
}
},
{ immediate: false }
);
这个监听函数处理不同场景下的内容更新:
- 非助手消息(用户消息)
- 非流式输出
- 流式输出的初始内容
- 流式输出的增量更新
与Markdown渲染结合
为了支持Markdown格式,我们还需要一个计算属性来处理文本内容:
const processedText = computed(() => {
if (!displayContent.value && !props.content) return "";
const textToProcess = displayContent.value || props.content;
// 缓存处理结果,避免重复计算
if (textToProcess === lastProcessedText.value) {
return lastProcessedResult.value;
}
try {
let processedText = textToProcess;
if (!processedText.trim()) return "";
// 处理特殊标签(如思考过程)
let hasThinkTag = processedText.includes("<think>");
if (hasThinkTag) {
// 处理完整标签
if (processedText.includes("</think>")) {
processedText = processedText.replace(
/<think>([\s\S]*?)<\/think>/g,
(match, p1) => {
return `<details class="think-details" ${
thinkDetailsOpen.value ? "open" : ""
}><summary>思考过程</summary><div class="think-content">${p1}</div></details>`;
}
);
}
// 处理不完整标签
else if (processedText.includes("<think>")) {
let parts = processedText.split("<think>");
if (parts.length > 1) {
let beforeThink = parts[0];
let thinkContent = parts[1] || "";
processedText =
beforeThink +
`<details class="think-details" ${
thinkDetailsOpen.value ? "open" : ""
}><summary>思考中...</summary><div class="think-content">${thinkContent}</div></details>`;
}
}
}
// 渲染Markdown
let renderedHtml = md.render(processedText);
// 更新缓存
lastProcessedText.value = textToProcess;
lastProcessedResult.value = renderedHtml;
return renderedHtml;
} catch (error) {
console.error("格式化内容时出错:", error);
return textToProcess ? md.render(textToProcess) : "";
}
});
打字效果的CSS实现
CSS部分同样重要,它为打字效果提供了视觉上的支持:
/* 打字机效果样式 */
.typing-effect {
min-height: 20px;
position: relative;
/* 添加字体渲染优化属性 */
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-rendering: optimizeLegibility;
/* 避免子像素渲染导致的模糊 */
transform: translateZ(0);
/* 确保文本锐利清晰 */
backface-visibility: hidden;
}
/* 光标动画 */
@keyframes blink {
0%,
100% {
opacity: 1;
}
50% {
opacity: 0;
}
}
错误处理与可靠性
为了确保组件的可靠性,我们添加了全面的错误处理和回退机制:
// 组件内错误处理器
const handleError = (err) => {
console.error("消息渲染错误:", err);
// 尝试清理所有可能导致问题的状态
try {
// 重置渲染器
if (markdownRenderer) {
try {
if (typeof markdownRenderer.clear === "function") {
markdownRenderer.clear();
}
} catch (e) {
// 忽略清理错误
}
markdownRenderer = null;
}
// 重置内部状态
clearTypingContent();
// 如果有内容,使用最简单的方式显示
if (props.content) {
displayContent.value = props.content;
currentContentBuffer.value = props.content;
}
} catch (e) {
console.error("错误恢复失败:", e);
}
};
// 使用Vue的onErrorCaptured生命周期钩子
onErrorCaptured(handleError);
性能优化
整个实现中包含多项性能优化:
- 局部更新而非全量更新:流式输出时只处理新增内容
- 使用requestAnimationFrame:减少重绘提高性能
- 动态调整处理速度:根据队列长度自适应调整
- 结果缓存:避免重复计算和渲染
- 智能块大小:根据内容类型动态调整处理块大小
核心变量解析与流程图
在实现打字效果的过程中,有几个核心变量起着至关重要的作用。下面详细解释这些变量的含义和它们在整个流程中的变化:
核心变量含义
-
displayContent:
- 含义:最终显示给用户的内容
- 类型:响应式引用(ref)
- 作用:直接绑定到UI上,用户看到的实际内容
-
newContent:
- 含义:从服务器接收到的最新内容
- 类型:函数参数
- 作用:表示LLM返回的最新完整内容,每次流式更新时都会更新
-
currentContentBuffer:
- 含义:当前已处理的内容缓冲区
- 类型:响应式引用(ref)
- 作用:保存当前已经处理过的内容,用于与新内容比较以确定增量部分
-
typingQueue:
- 含义:打字效果的字符队列
- 类型:响应式引用(ref)数组
- 作用:存储待显示的内容片段,按顺序弹出并显示
-
contentChunk:
- 含义:从队列中取出的当前要显示的内容片段
- 类型:局部变量
- 作用:表示当前正在处理的内容片段,将被设置到displayContent中
变量变化流程
当LLM流式返回内容时,这些变量的变化遵循以下流程:
-
初始状态:
- displayContent = ""
- currentContentBuffer = ""
- typingQueue = []
- isTyping = false
-
接收第一段内容:
- newContent = "你好"
- 调用processStreamContent("你好")
- 创建字符队列:typingQueue = ["你", "你好"]
- 启动打字效果处理
-
处理队列第一项:
- contentChunk = "你"(从队列中弹出)
- displayContent = "你"
- currentContentBuffer = "你"
- 队列变为:typingQueue = ["你好"]
-
处理队列第二项:
- contentChunk = "你好"(从队列中弹出)
- displayContent = "你好"
- currentContentBuffer = "你好"
- 队列变为:typingQueue = []
- 打字效果暂停(isTyping = false)
-
接收增量更新:
- newContent = "你好,世界"
- 计算增量部分:",世界"
- 将增量部分添加到队列:typingQueue = ["你好,", "你好,世", "你好,世界"]
- 重新启动打字效果处理
-
继续处理队列:
- 依次处理队列中的每一项,更新displayContent和currentContentBuffer
- 最终状态:displayContent = "你好,世界", currentContentBuffer = "你好,世界", typingQueue = []
特殊情况处理
-
内容修正:
- 如果newContent长度小于currentContentBuffer,说明内容被修正
- 直接设置displayContent = newContent,清空队列
-
重复内容:
- 如果contentChunk与currentContentBuffer相同,跳过处理
- 避免不必要的UI更新
-
动态速度调整:
- 根据typingQueue长度动态调整处理速度
- 队列越长,处理速度越快
PUML流程图
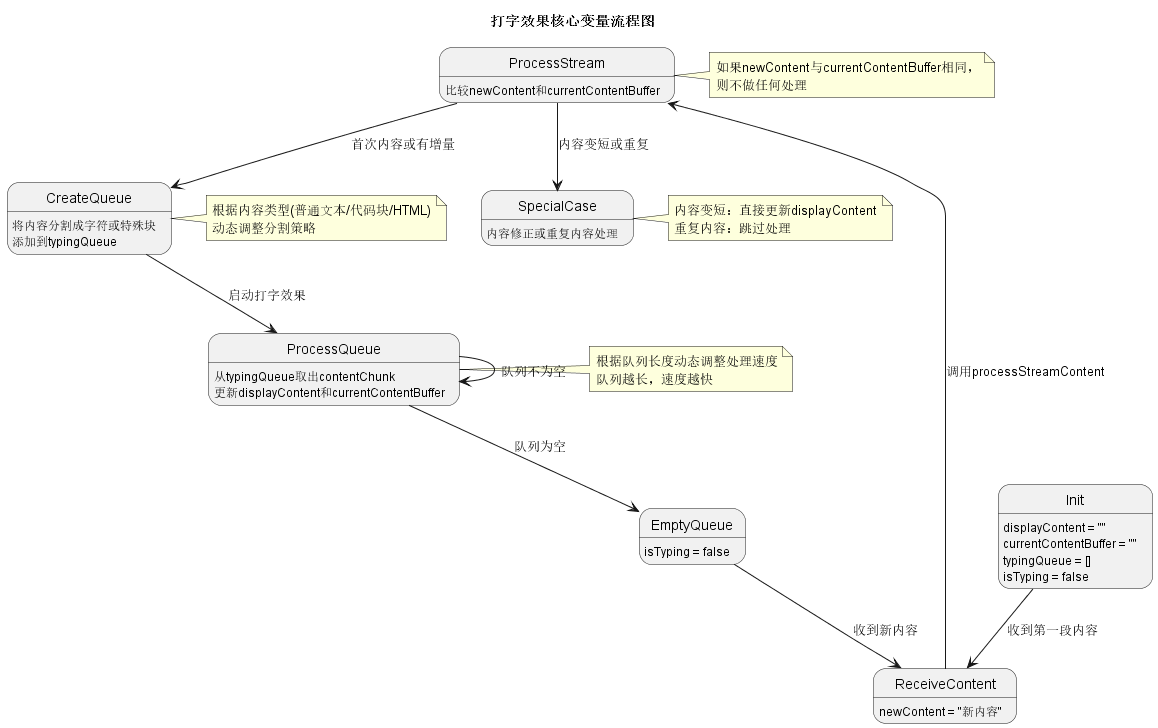
变量关系总结
-
数据流向:
newContent → typingQueue → contentChunk → displayContent/currentContentBuffer -
状态同步:
- displayContent与currentContentBuffer在正常情况下保持同步
- currentContentBuffer用于与newContent比较以确定增量部分
- typingQueue作为中间缓冲区,控制内容显示的速度和节奏
-
优化策略:
- 只处理增量部分,避免重复处理
- 动态调整处理速度,提高用户体验
- 特殊内容完整处理,保证渲染正确性
通过这种设计,实现了既流畅自然又高效可靠的打字效果,为用户提供了更好的交互体验。
总结
这种实现LLM流式输出打字效果的方案有几个显著优势:
- 流畅自然的打字效果:通过字符级队列和动态速度调整实现
- 特殊内容处理:正确处理代码块、HTML标签等特殊内容
- 高性能:使用多种技术确保在大量文本处理时依然保持流畅
- 可靠性:包含全面的错误处理和回退机制
- 与Markdown无缝集成:支持丰富的格式化输出
这种实现方式不仅适用于LLM聊天应用,也可以应用于其他需要打字效果的场景,如教学演示、交互式文档等。通过将这些技术应用到你的项目中,可以显著提升用户体验和应用的专业感。

评论区